Can you start a Roth IRA without a job?
What is the difference between a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA?
Contents
With a Roth IRA, you contribute dollars after tax, your money grows tax-free, and you can generally make tax- and penalty-free withdrawals after the age of 59½. With a traditional IRA, you contribute dollars before or after tax, your money grows tax-deferred, and payments are taxed as current income after the age of 59½.
What is better a Roth IRA or a traditional IRA? In general, you are better off in a traditional if you expect to be at a lower tax level when you retire. … If you expect to be in the same or higher tax bracket when you retire, you can instead consider contributing to a Roth IRA, which allows you to settle your tax bill now rather than later.
Why traditional IRA is better than Roth?
The biggest difference between a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA is how and when you get a tax deduction. Contributions to traditional IRAs are deductible, but pension payments are taxable. By comparison, contributions to Roth IRAs are not deductible, but retirement benefits are tax-free.
Why would you want a traditional IRA?
A traditional IRA is more appropriate for people who want to be in a zero or very low tax when they retire. They get the benefit of the tax deduction on contributions and no tax on withdrawal. If you do not anticipate the need to draw on your IRA upon retirement, you will also want to fund a Roth IRA.
Why does a traditional IRA have the best tax advantages?
The main benefits of having a traditional IRA are the tax deduction for contributions, the tax-deferred investment mix, and the ability to invest in just about any stock, bond, or mutual fund you want.
What are the 3 types of IRA?
There are several types of IRAs:
- Traditional IRA. Contributions are typically deductible. …
- Roth IRA. Payments are made with funds after tax and are not deductible, but earnings and withdrawals are tax-free.
- SEP IRA. …
- SIMPLE IRA.
How do I know if I have a traditional or Roth IRA?
If you are unsure of the type of IRA you have, you should check the paperwork you received when you first opened the account. It will explicitly indicate the type of account in question.
What is the downside of a Roth IRA?
One important drawback: Roth IRA contributions are provided with money after tax, which means there is no tax deduction in the contribution year. Another disadvantage is that account earnings must not be withdrawn until at least five years have passed since the first contribution.
When would you not want a Roth IRA?
Roth IRA single-file contributions are prohibited if your income is $ 140,000 or more in 2021. The income-phasing-out range for singles is $ 125,000 to $ 140,000. Single taxpayers can not contribute to a Roth in 2022 if they earn $ 144,000 or more. Your contribution will be reduced if you earn between $ 129,000 and $ 144,000.
Is a Roth IRA good or bad?
Roth IRAs may seem ideal, but they have drawbacks, including the lack of an immediate tax deduction and a low maximum contribution. … In a world of retirement accounts, Roth IRAs are the favorite child. What is there not to love about completely tax-free growth on your retirement savings?
Can self employed contribute to Roth IRA?
An IRA is probably the easiest way for the self-employed to start saving up for retirement. There are no special filing requirements and you can use it whether you have employees or not. … One note: The Roth IRA has income limits for eligibility; those who earn too much can not contribute.
Why should you start saving up for emergencies? Why an emergency fund is so important An emergency fund is an essential part of a solid financial plan. Emergency funds allow you to cover unexpected expenses without having to use high-interest credit cards or take out a loan. Therefore, today is the time to start saving up for an emergency. … Unexpected medical expenses.
How do I start an emergency savings?
Start an emergency fund
- Map your monthly income and expenses. If you have already read through Track Your Spending, just go back to your worksheet to see what your monthly expenses are. …
- Set your emergency savings goal. …
- Develop a plan to start saving. …
- Put your emergency fund in an accessible place. …
- Stick to your plan.
What is a good amount to have in emergency savings?
Most experts recommend keeping three to six months of expenses in an emergency fund, but some situations justify more. Some experts recommend a small emergency fund while paying off on debt. If your job is secure and you do not have a lot of expenses, you may be able to save less.
How much does it cost to start an emergency fund?
Most financial experts recommend that you have somewhere between three months and six months of basic living expenses in your emergency fund. The three-month guideline is generally recommended for those who are in paid positions and have a more secure job.
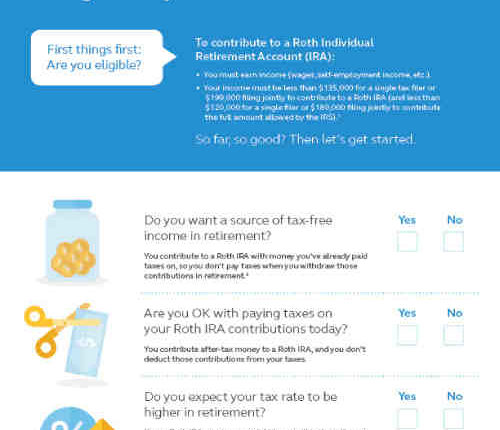
Do you need earned income to contribute to a traditional IRA?
Traditional IRA Contribution Rules Having a working income is a requirement for contributing to a traditional IRA, and your annual contributions to an IRA cannot exceed what you earned that year. Otherwise, the annual contribution limit is $ 6,000 in 2021 and 2022 ($ 7,000 if you are 50 years or older).
What type of income qualifies for an IRA contribution? As a single file, you can make a full contribution to a Roth IRA if your adjusted adjusted gross income is less than $ 124,000 by 2020. For 2021, you can make a full contribution if your adjusted adjusted gross income is less than $ 125,000.
Do you need taxable income to contribute to an IRA?
Contribution. To contribute to a traditional IRA, if you file a joint return, you and / or your spouse must have taxable compensation, such as salary, salary, commission, tips, bonuses, or net income from self-employment.
What happens if you contribute to an IRA without earned income?
If you have not earned any compensation from work but still made a contribution to your IRA, the amount you have contributed will be subject to 6 percent penalty tax on excess contributions. The penalty tax will be applied each year where the excess contribution remains in your IRA.
Can you contribute to an IRA if you have no taxable income?
Can you put money into an IRA or a Roth IRA if you do not have a wage income? … In fact, contributions to both traditional and Roth IRAs can only be made from what the IRS determines as “income income” or taxable compensation.
What happens if you contribute to an IRA without earned income?
If you have not earned any compensation from work but still made a contribution to your IRA, the amount you have contributed will be subject to 6 percent penalty tax on excess contributions. The penalty tax will be applied each year where the excess contribution remains in your IRA.
Can you contribute to an IRA if you have no earned income?
In general, if you do not earn any income, you can not contribute to either a traditional or a Roth IRA. In some cases, however, married couples who file a joint application may be able to make IRA contributions based on the taxable compensation reported on their joint return.
How much can I contribute to my IRA if I am unemployed?
However, you can not contribute more than your earned income. This means that if you only earned a total of $ 5,000 in salary and self-employment income for the year before you went into unemployment, you can not contribute more than $ 5,000 to your IRAs.
Is earned income required for traditional IRA?
Anyone with adequate working income can contribute to an IRA. … In order to be eligible for IRA / Roth earned IRA contributions Income is traditionally from work, so it includes salaries, wages, tips, bonuses, commissions and positive net income from self-employment. It also includes received taxable alimony.
Can you contribute to traditional IRA without earned income?
Can you put money into an IRA or a Roth IRA if you do not have a wage income? … In fact, contributions to both traditional and Roth IRAs can only be made from what the IRS determines as “income income” or taxable compensation.
Is rent considered earned income?
Rental income is not earned income due to the source of the money. Instead, rental income is considered passive income with few exceptions.
Is rent earned or unearned income? Net rental income is unearned income unless it is earned income from self-employment (e.g., a person who is in the process of renting property).
Can you count rental income as income?
Generally, rental income can be counted when you apply for a mortgage or refinance an investment property. However, like all other sources of income, it must be duly documented and meet specific qualifying guidelines.
How do Underwriters calculate rental income?
If the tenant has a tenant, lenders will take a percentage of the income outlined on a lease and use it to determine the expected rental income. They usually spend 75% of your total reported income – 25% is deducted to take into account potential vacancies and ongoing maintenance.
How do you calculate rental income on Schedule E?
When using Form E, determine the number of months the property was in operation by dividing the fair rental days by 30. If fair rental days are not reported, the property is considered to be in operation for 12 months unless there is evidence of a shorter service life.
Can I convert my IRA to a Roth?
You can convert all or part of the money in a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA. … You will owe tax on the money you convert, but you will be able to take tax-free withdrawals from the Roth IRA in the future.
How do I convert my IRA to a Roth without paying taxes? If you want to make a Roth IRA conversion without losing money on income tax, you should first try to do so by rolling your existing IRA accounts into your employer’s 401 (k) plan and then converting non-deductible IRA contributions forward.
How much can you convert from a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA per year?
The government only allows you to contribute $ 6,000 directly to a Roth IRA in 2021 and 2022 or $ 7,000 if you are 50 years or older, but there is no limit to how much you can convert from tax-deferred savings to your Roth IRA in a single year.
How much can I transfer from my traditional IRA to Roth?
There is no limit to how much you can convert. Here are the three ways to get your money from a traditional account to a Roth: Indirect rollover. You will receive a distribution check from your traditional IRA and then contribute to your Roth IRA within 60 days.
How much can you rollover into a Roth IRA each year?
You are also subject to annual Roth IRA limits ($ 6,000 for fiscal year 2020 and $ 6,000 for fiscal year 2021. If you are 50 years or older, $ 7,000 for fiscal year 2020 and $ 7,000 for fiscal year 2021). And these limits are reduced – and phased out gradually – as your adjusted adjusted gross income increases.
Can I move my IRA to a Roth IRA?
You can transfer some or all of your existing traditional IRA (or other retirement account) balance to a Roth IRA, regardless of your income. But keep in mind that income eligibility restrictions still apply to this year’s contributions.
How much tax will I pay if I convert my IRA to a Roth?
Converting a traditional $ 100,000 IRA to a Roth account in 2019 would result in about half of the extra income from the conversion being taxed at 32%. But if you spread the $ 100,000 50/50 conversion over 2019 and 2020 (which you are allowed to), all the extra income from conversion is likely to be taxed at 24%.
What is the penalty for converting a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA?
The 10% penalty for early distribution does not apply to assets that you convert to a Roth IRA, even if you convert the assets before you reach the age of 59½. Any amount distributed that is not converted (e.g. funds used to pay your tax bill) may be subject to 10% pre-distribution.
Is it a good idea to convert IRA to Roth IRA?
The bottom line A Roth IRA conversion can be a very powerful tool for your retirement. If your taxes increase because of government increases – or because you earn more, a Roth IRA conversion can save you significant tax money in the long run by putting you in a higher tax bracket.
How do I avoid taxes on a Roth IRA conversion?
The so-called back door Roth is a way to avoid a big tax bill when you earn more than the income limit of a Roth. In that case, if you are also covered by an employer pension scheme like a 401 (k), you would probably not be able to fund a deductible IRA because of the IRS rules.
What is the penalty for converting a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA?
The 10% penalty for early distribution does not apply to assets that you convert to a Roth IRA, even if you convert the assets before you reach the age of 59½. Any amount distributed that is not converted (e.g. funds used to pay your tax bill) may be subject to 10% pre-distribution.
Who is not allowed to open a Roth IRA?
If your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is more than $ 196,000 for jointly married or $ 133,000 for single files, you cannot make a Roth contribution.
Can anyone qualify for Roth? Roth IRA contributions are limited by income level. Generally, you can contribute to a Roth IRA if you have taxable income, and your adjusted adjusted gross income is either: less than $ 194,000 (phasing out from $ 184,000) if you are married, filing a joint application.
Who is not permitted to open an IRA?
Age limit. To open a traditional IRA and make contributions, you must not reach the age of 70½ by the end of the year. If you are older than that, you are not allowed to open a traditional IRA because you are prohibited from making deposits to it. This age limit applies even if you are still working and not retired.
Can everyone open an IRA?
Understanding IRAs Anyone who has earned income can open an IRA. It includes people who have a 401 (k) through an employer. The only limitation is on the total amount they can contribute in a single year through pension accounts while still receiving tax benefits.
Are there any limitations on who can have an IRA?
It depends on what kind of IRA it is. Almost anyone can contribute to a traditional IRA, provided you (or your spouse) receive taxable income and you are under 70 years of age. However, your contributions are only tax deductible if you meet certain qualifications.
Comments are closed.